Let’s learn about the algorithms and flowcharts in Programming today.
What is a Computer Programming?
Computer programming is also known as programming. It is a process that actually leads from an original formulation of a computer problem to executable computer programs. Most important to know, a computer program is usually written by a computer programmer in a programming language itself. It is important because it defines the relationship, grammar and semantics which ultimately helps the programmer to communicate effectively with the machines that they program.
A typical programming task can be divided into two phases:
- Problem-solving phase
- Produce an ordered sequence of steps that describe the solution of the problem
- This sequence of steps is called an algorithm
- Implementation phase
- Implement the program in some programming language
Algorithms and flowcharts are two different tools used for creating new programs. So, knowing both of them well in advance is a great idea to start programming easily.
Algorithm
An algorithm is a well-defined procedure that allows a computer to solve a problem. In computer science, an algorithm is a step-by-step procedure for calculations. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning. Basically, it can be presented by natural languages, pseudo code and flowcharts, etc.
Characteristics of a Good Algorithm
- Precision: The steps are precisely defined in an algorithm to give accurate results.
- Uniqueness: Results of each step are unique and defined. And, the result depends on the input and the result of the previous step.
- Finiteness: The algorithm ultimately stops itself when a finite number of instructions are executed.
- Easy modifications: In algorithm, you can easily make modifications that make the process easier.
- Easy and simple to understand: The steps are easy and understandable to the non-programmers too.
Solved Examples
Example 1: Print 1 to 10:
Algorithm:
Step 1: Initialize X as 0,
Step 2: Increment X by 1,
Step 3: Print X,
Step 4: If X is less than 10 then you need to repeat the step 2.
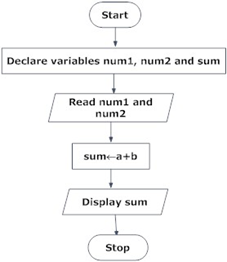
Example 2: Convert Temperature from Fahrenheit (℉) to Celsius (℃)
Algorithm:
Step 1: Read temperature in Fahrenheit,
Step 2: Calculate temperature with formula C=5/9* (F-32),
Step 3: Print C,
Flowchart
A schematic representation of a sequence of operations, as in a manufacturing process or computer program is known as a flowchart or we can say flowchart is a graphical representation of the sequence of operations in an information system or program.
Basic Characteristics of Flowchart
- It shows the logic behind the algorithm.
- It literally emphasizes individual steps and their interconnections.
- It clearly illustrates the flow of programming techniques, they are a valuable tool in the education of programmers
- control flow from one action to the next action.
Types of Flowchart
There are four general types of a flowchart
- Document flowcharts, which shows controls over a document flow through a defined system.
- Data flowcharts, which shows controls over a data flow in a system.
- System flowcharts, which shows controls at a physical or resource level.
- Program flowchart, which shows the controls in a program within a system.
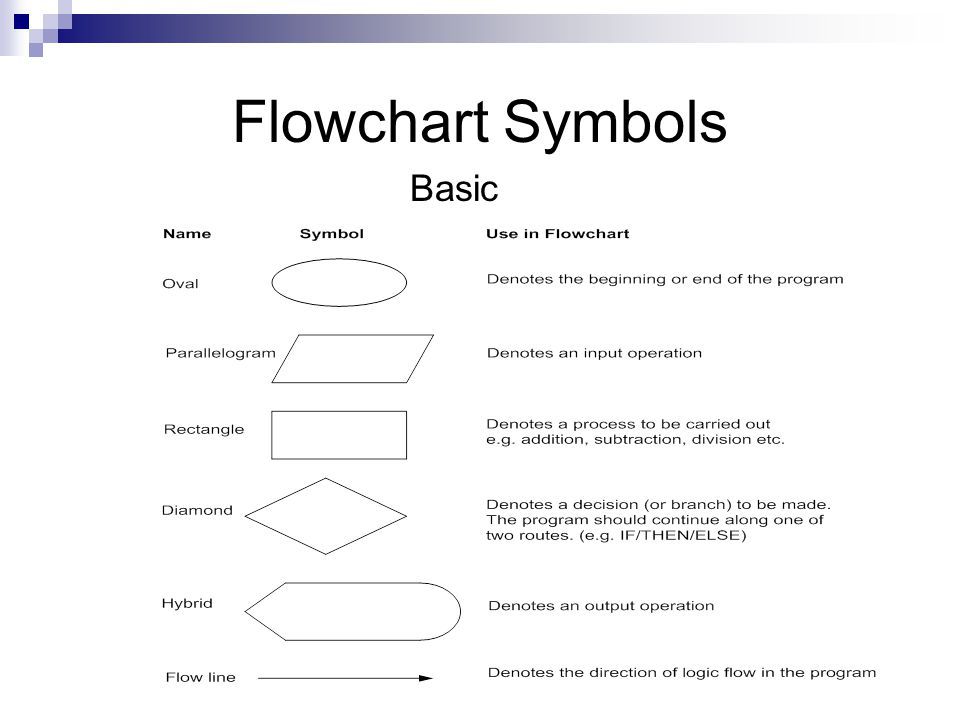
Pseudocode in Programming
- The pseudocode in programming is generally a detailed yet readable description of what a computer program or algorithm must do.
- The main important thing about pseudocode is that it is not in the programming language, rather it is in formally style natural language.
- Thus, enabling easy work. Sometimes, pseudocode is used as an important and detailed step in the process of developing a program.
Both algorithm and pseudocode are two different things. But, you can base your pseudocode on an algorithm that is the thing, They are used to plan out programs.
Solved Examples
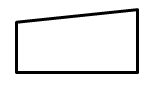
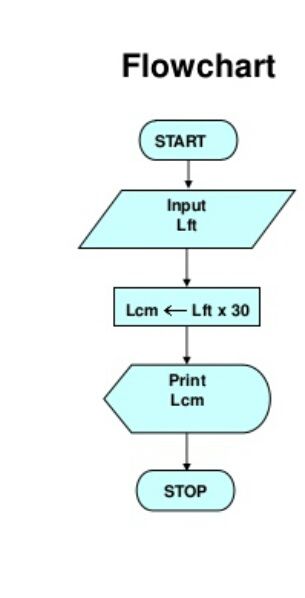
Example 1: Draw a flowchart to convert the length in feet to centinmeter.
Flowchart:
Here, Pseudocode is used.
- Input the length in feet (Lft)
- Calculate the length in cm (Lcm) by multiplying LFT with 30
- Print length in cm (LCM)
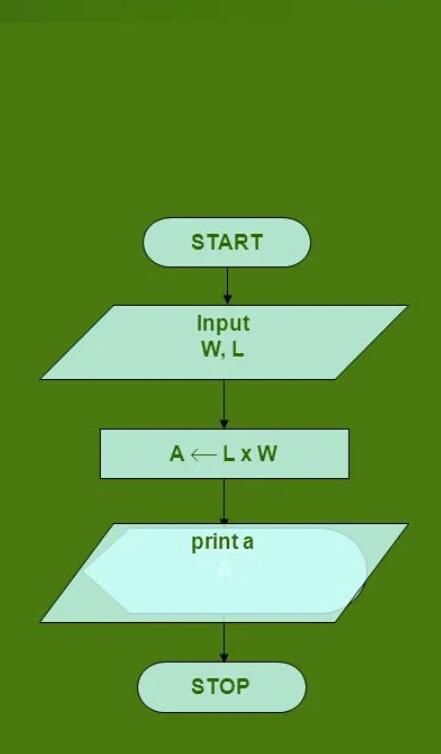
Example 2: Draw a flowchart that will read the two sides of a rectangle and calculate its area.
Flowchart:
Here Pseudocode is used.
- Input the width (W) and length (L) of a rectangle.
- Calculate the area (A) by multiplying L with W.
- Print A
Recap
- The basic knowledge about computer programming and basic two tools used in it; algorithm and flowchart.
- An algorithm is a well-defined procedure that allows a computer to solve a problem well explained with the help of examples.
- Characteristics of a good algorithm.
- A schematic representation of a sequence of operations, as in a manufacturing process or computer program is known as a flowchart, The basic characteristics and its types.
- Basic Flowchart symbols and their use.
- The pseudocode in programming is generally a detailed yet readable description of what a computer program or algorithm must do. Different from an algorithm.
- Flowchart well explained through examples having pseudocode.