Have you ever wondered which genius mind on this earth thought of inventing such useful device for the mankind? It all started with one simple tool we all have heard about, The Abacus! With respect to class 6 History and Generation of Computers, let us study how and when did it led to the invention of computers.
History of Computers


- The first computers did not have monitors or memory. The abacus, the adding machine was invented in Babylon in 500 B.C.
- It was used to count and keep track of money and other numerical things.
- Famous mathematicians invented calculators using gears and wheels.
- In 1833, Charles Babbage invented all the parts the modern computer uses, but it wasn’t until 120 years later that the first modern computers were invented.
- These first computers were huge and took up a whole room.
- The beginnings of computers as we know them happened in 1980 – only 30 years ago. Now we will study the evolution of computers
Generation of Computers
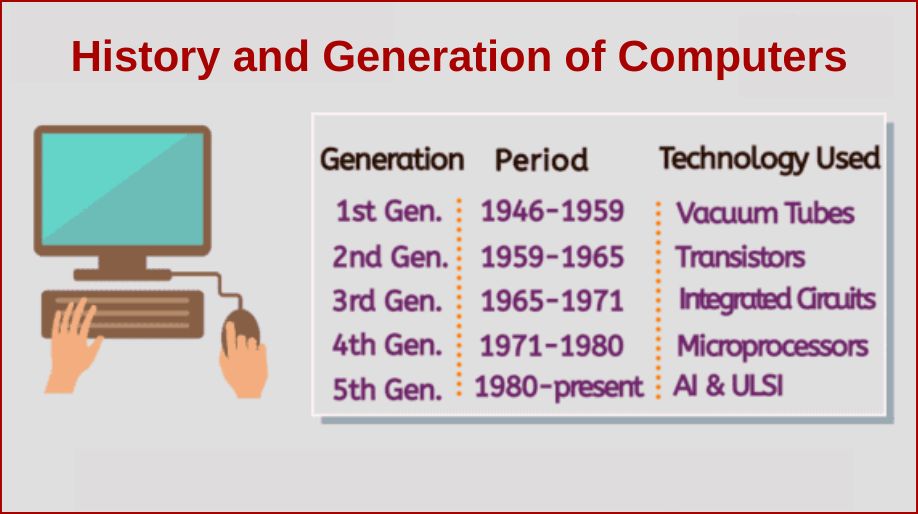
Computers have evolved and advanced significantly over the decades since they were invented. The history of computer development is grouped into different generations of computer. A generation refers to the change in technology. The computers are classified into five generations based upon the change in architecture, languages, modes of operation, etc. They are:
- First Generation Computer (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computer (1957-1963)
- Third Generation Computer (1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computer (1972 onward)
- Fifth Generation Computer (Present and future)
First Generation Computer (1940-1956)
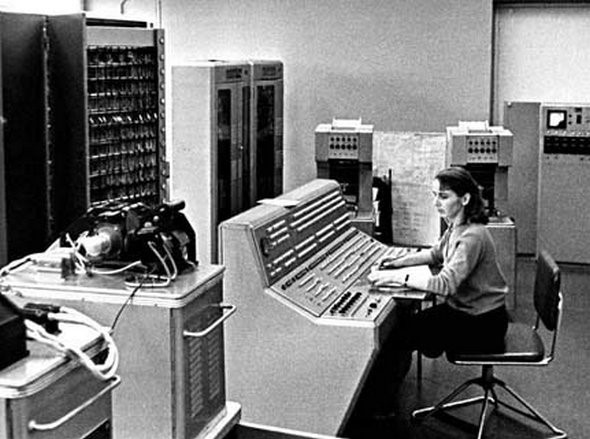

The first generation computers were used during 1940-1956. They were based on vacuum tubes.
Characteristics of First Generation computers are:
- Vacuum tubes were used in circuits.
- These computers are very large in size.
- Programming for this generation was done using machine language.
- They were very expensive and require a large amount of electricity.
- They produce more heat.
- These computers could calculate data in a millisecond.
Examples of First Generation computers are: ENIVAC and UNIVAC-1.
Second Generation Computer (1957-1963)

As transistors developed, it helped in generating computers better than First Generation.
Characteristics of Second Generation computers are:
- Vacuum tubes were replaced by transistors in circuits.
- These computers were smaller in size.
- They produced less amount of heat.
- They required less amount of electricity as compared to First Generation computers.
- These computers used Assembly language instead of Machine language.
- These computers could calculate data in a microsecond.
Examples of Second Generation computers are IBM 1920, IBM 1401, etc.
Third Generation Computer (1964-1971)

During the period of 1964 to 1971, Third generation computers were developed.
Characteristics of Third Generation computers are:
- Transistors were replaced by Integrate Circuits. Multiple transistors were placed on a silicon chip. This reduced the size of computers enormously.
- These computers used lesser power and generated lesser heat.
- Operating system and other application software were used.
- These computers were general purpose computers. They were used for commercial purposes.
- These computers could calculate data in a nanosecond.
- High-level languages were introduced.
Examples of third generation computers are IBM-360 series, CDC 1700, etc.
Fourth Generation Computer (1972 onward)

The computers that we use for daily purposes are from the Fourth Generation.
Characteristics of Fourth Generation computers are:
- Large-scale integration and Very large scale integration. Technologies are used. These technologies allowed the integration of thousands and millions of transistors on a small silicon chip.
- High-level languages like C and C++ are used.
- Operating systems like MS-DOS and Windows were developed and introduced.
- The computation speed increased to picoseconds.
- Microprocessors are developed.
- Computers now have become much smaller, faster and more reliable. They use less electricity and generated less heat.
Examples of Fourth generation computers are CRAY- 1, Apple, etc.
Fifth Generation Computer (Present and future)
Fifth Generation computers are still in development.
Characteristics of Fifth Generation computers are:
- It is based on the technique of Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- A computer can understand spoken words.
- Currently, scientists are working to increase the processing power of computers.
- They are trying to create a computer with real IQ with the help of advanced programming and technologies.
Examples of Fifth generation computers are IBM notebooks, PARAM 10000, etc.
Solved examples with respect to class 6 computer lessons are -
- Who invented all the parts the modern computer uses? And when?
Ans: Charles Babbage in 1833.
- Which generation of computer did programming using machine language?
Ans: First Generation.
- What was used to replace Vacuum in Second Generation?
Ans: Transistors.
- In which generation, Operating system and other application software was used?
Ans: Third Generation.
- In Fourth Generation, The computation speed increased to?
Ans: Picoseconds.
With respect to class 6 History and Generation of Computers, classification of computers
On the basis of size, Computers are divided into four categories. They are -
- Supercomputers
- Mainframe Computers
- Minicomputers
- Microcomputer
Supercomputers
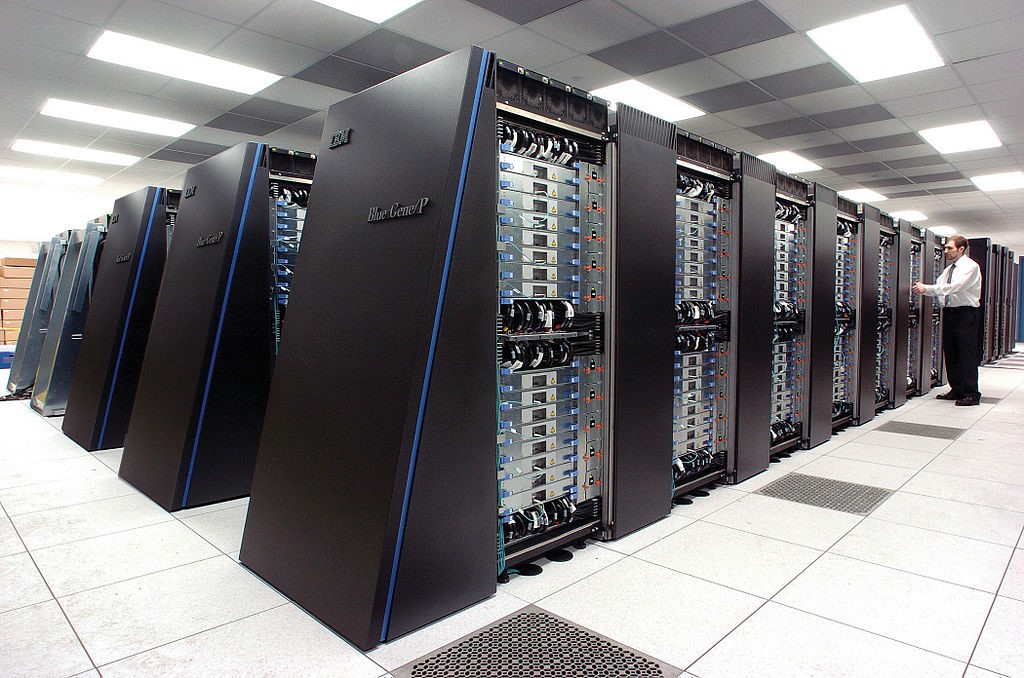

A supercomputer is a computer which has a high level of performance. They are very expensive, very fast, and the most powerful computers. They have a large storage capacity. They can perform a large number of calculations in a fraction of a second.
Supercomputers are used for several fields. Some of them are -Space Exploration, Earthquake studies, Weather Forecasting, etc.
Example of supercomputers are: IBM Sequoia , PARAM, PACE, etc.
Mainframe computers
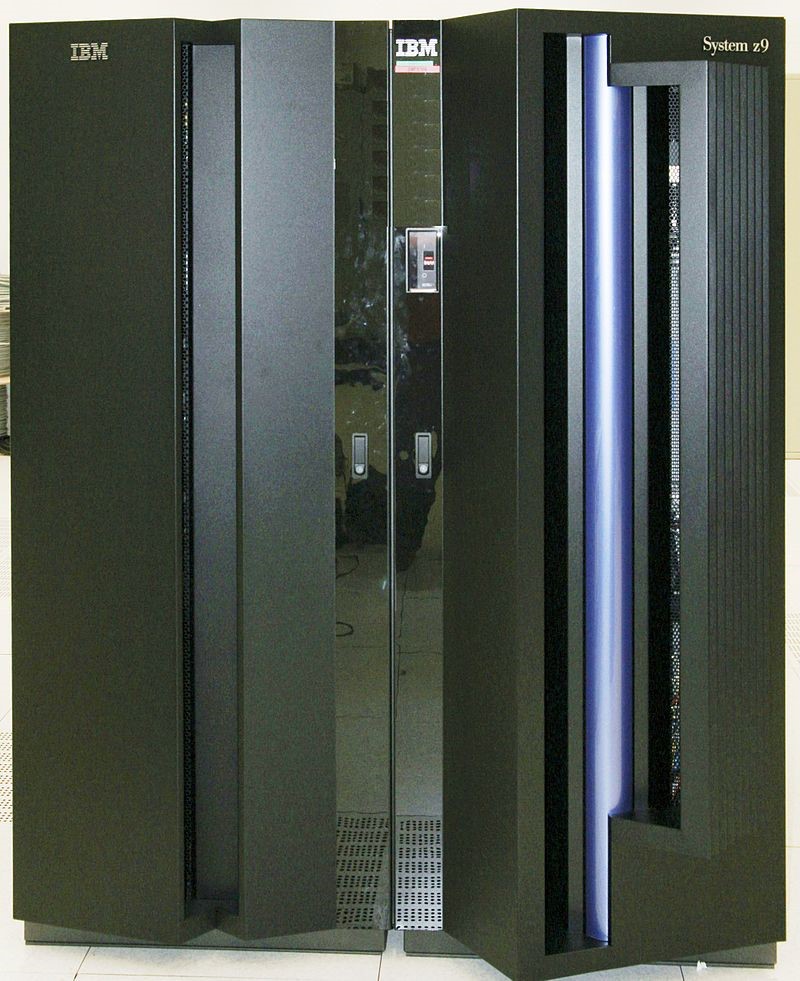

A mainframe computer is a powerful computer used in many large organizations that need to manage a large amount of data. They have less processing speed and storage capacity as compared to supercomputers. Mainframe computers can process complex mathematical calculations.
Example of mainframe computers are: ICL39, CDC 6600, VAX 8842 System z9.
Minicomputers
Minicomputers are also known as “Midrange Computers". Minicomputers are multiuser computers where many users can simultaneously work on the computers. They have less storage capacity than mainframe computers. They are smaller in size. Minicomputers are used in university, large business, scientifically researched.
Examples of minicomputers are PDP-11, VAX, 7500 MAGNUM etc.
Microcomputers
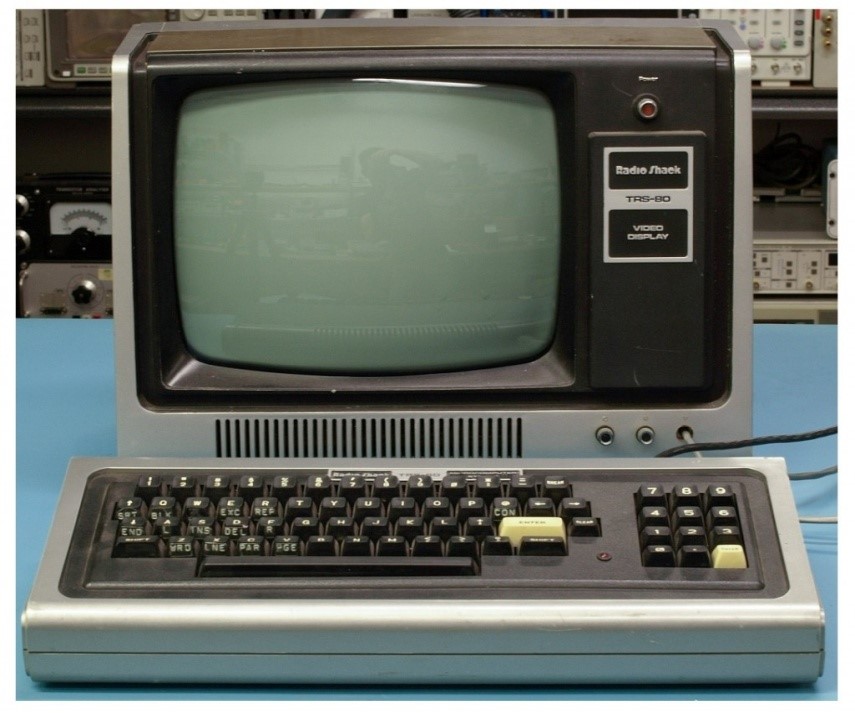

Microcomputers are also referred to as Personal computers. They are a type of computers designed for single user tasks. They are small in size and are the cheapest. They are easy to operate.
Microcomputers are widely used in educational institutes, home, etc.
Examples of microcomputers are IBM PC, Apple, etc.
Examples-
- Which computer has a high level of performance?
Ans: Supercomputer.
- Microcomputers are also referred as?
Ans: Personal computers.
- Minicomputers are ____computers.
Ans: Multiuser.
Recap
- In 1833, Charles Babbage invented all the parts the modern computer uses.
- The computers are classified into five generations based upon the change in architecture, languages, modes of operation, etc. They are -
- First Generation Computer (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computer (1957-1963)
- Third Generation Computer (1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computer (1972 onward)
- Fifth Generation Computer (Present and future)
- First Generation Computers used vacuum tubes were used.
- Second Generation Computers used transistors.
- Transistors were replaced by Integrate Circuits in Third Generation.
- Large-scale integration and Very large scale integration technologies were used in the Fourth Generation.
- Fifth Generation computers are currently being developed.
- Computers are divided into four categories. They are Supercomputers, Mainframe Computers, Minicomputers and Microcomputer.
- The supercomputer has the highest level of performance out of the four types of computers.
- Microcomputers are widely used in home, schools, etc.