Memory
- With respect to class 8 Memory and Storage Devices, memory is the storage device that facilitates the remembrance power to a computer system.
- It refers to the physical devices used to store programs (sequences of instructions) or data on a temporary or permanent media in a computer.
- Any information stored in the computer systems that are fast (i.e. RAM) is the primary memory.
- Secondary memory is a physical device for program and data storage which are slow to access but offer higher memory capacity.
- Primary memory stored on secondary memory is called virtual memory.
- Primary Memory can be categorized as Volatile Memory & Non-Volatile Memory.
Volatile memory (RAM): With respect to class 8 computer lessons, volatile memory requires power to maintain the stored information. Most modern semiconductor volatile memory is either Static RAM or dynamic RAM.
Static RAM: With respect to class 8 computer lessons, until it is connected to the power supply it retains the contents and is easy to interface too but uses six transistors per bit.
Dynamic RAM: Complicated to interface and control and also needs a regular refresh cycle to prevent the contents being lost.
Non Volatile Memory (ROM): With respect to class 8 computer lessons, non-volatile memory is computer memory that can retain the stored information even when not connected to power supply. Examples of non-volatile memory are the flash memory and ROM/PROM/EPROM/EEPROM memory (used for firmware such as boot programs).
Cache Memory: With respect to class 8 Memory and Storage Devices, it is an auxiliary memory, from which high-speed retrieval is possible.
Storage devices with respect to class 8 Memory and Storage Devices
Need for storage in a computer –
- A computer cannot save or remember any information without storage.
- A computer can run with no storage device; however, we can only view the information.
- Even the simplest task like browsing the Internet requires information to be stored on your computer.
Multiple types of storage devices –
- Computers store huge data as we use computers in all fields.
- When new storage devices have launched the usage of previously used storage devices gets low.
- All recently invented storage devices hold more space and can have quick access.
- For example, in the initial stage, we used punch cards later came the floppy disks.
- Floppy disks are replaced by CD-ROM drives, which were replaced by DVD drives, which have been replaced by flash drives.
Storage location –
- It is the path or space where the information is saved to.
- When you try to save a document it will prompt you with the storage location, where you would like to save the information.
- Mostly all the information is saved to your computer hard drive.
- This information can be transferred to other devices with help of internet or portable devices.
With respect to class 8 computer lessons, what storage devices are used today?
- As we have developments every now and then most of the storage devices used earlier is no longer used with today's computers.
- Desktop computers with disc drives typically use a disc drive that is capable of reading CD's and DVD's and writing CD-R and other recordable discs.
With respect to class 8 computer lessons, what storage device has the largest capacity?
- The largest storage device for the personal computer is the hard drive or SSD.
- However, computers that are connected to networks have access to larger storage with large tape drives or cloud computing.
- We have two types of storage devices they are a primary storage device and a secondary storage device.
- Primary storage devices are like RAM.
- Secondary storage devices are like the hard disk which can be removable, internal, or external storage.
Examples of computer storage with respect to class 8 Memory and Storage Devices
Magnetic storage devices:
- This is one of the most common types of storage used in computers.
- Most of the external storage devices used this technology.
- Examples are -
- Floppy diskette
- Hard drive
- Magnetic strip
- Super Disk
- Tape cassette
- Zip diskette

Optical storage devices:
- This principle works using lasers and lights.
- Lasers and lights are used for reading and writing data.
- Examples are -
- Blu-ray disc
- CD-ROM disc
- CD-R and CD-RW disc

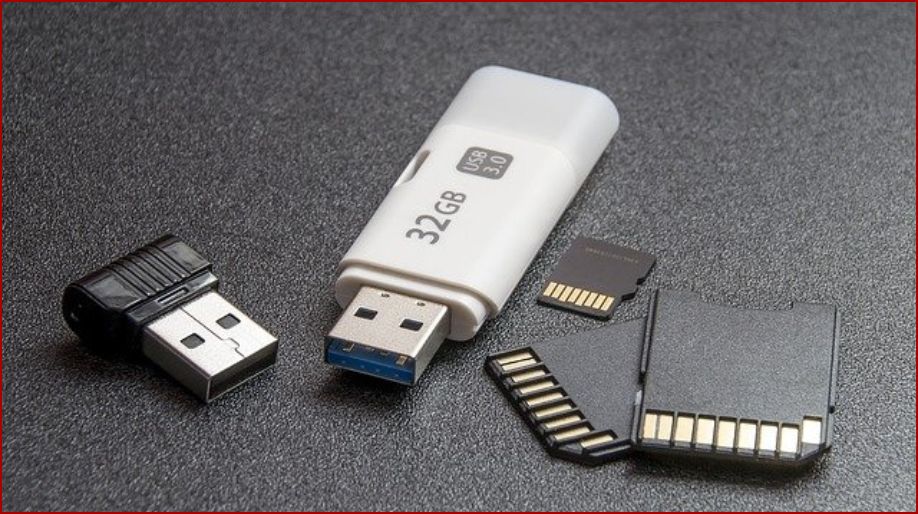
Flash memory devices with respect to class 8 Memory and Storage Devices
- As these storages were cheaper, efficient and reliable it replaced magnetic media.
- Examples are -
- USB flash drive
- Memory card
- Memory stick
- SSD

Online and cloud:
- To access data from more than one device now most trending storage media is to store data online and in clouds.
- Examples are -
- Cloud storage
- Network media
Paper storage:
- In earlier days for storing information, computers had no method of using any of the above technologies and had to rely on paper.
- These days, the below-given forms of storage are rarely used or found.
- Examples are -
- OMR (Optical Mark Recognition, OMR is the process of gathering information from human beings by recognizing marks on a document.)
- Punch card

Recap with respect to class 8 Memory and Storage Devices
Memory
- It is the storage device that facilitates the remembrance power to the computer system.
- Volatile memory (RAM): Volatile memory requires power to maintain the stored information. Most modern semiconductor volatile memory is either Static RAM or dynamic RAM.
- Non Volatile Memory (ROM): Non-volatile memory is computer memory that can retain the stored information even when not connected to power supply.
- Cache Memory: It is an auxiliary memory, from which high-speed retrieval is possible.
Storage devices -
- Need for storage in a computer
- Multiple types of storage devices
- Storage location
- Which storage devices are used today?
- What storage device has the largest capacity?
- Examples of computer storage