- It is a platform that manages all software and hardware on the computer.
- The main purpose of the operating system is to coordinate between these programs and to ensure all of these programs get what it needs.
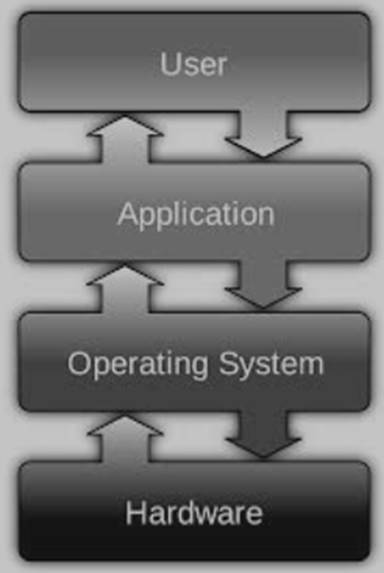
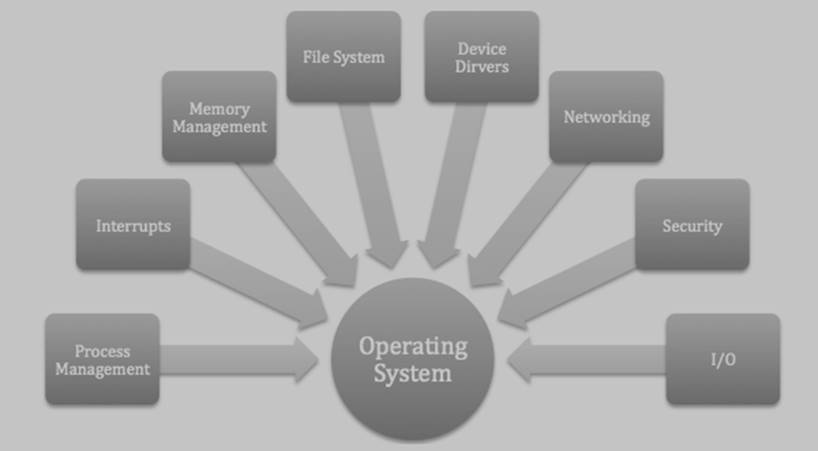
Functions of the operating system
Let us discuss the functions of the operating system in detail:
Processor management –
- The most important resource of any computer is a Processor.
- There will be several programs running on the computer at the same time. Each program requires a processor for its function. Operating system decides which process has to be allocated to the processor depending on when and how.
Memory management –
- The operating system acts as a memory manager.
- It decides which memory has to be allocated to a process.
- It also computes how much memory and how long the memory is to be allocated.
File management –
- The file manager allocates files and directories to processes.
- It helps the computer to read/write files either to a hard disk or any other external storage devices.
Device management –
- The operating system also manages the external devices.
- Devices that are attached to the computer such as a keyboard, mouse, speakers, microphone, etc.
- Most of the devices have a built-in device driver which is launched by the operating system for the device to work.
Types of operating systems
- Operating systems usually come pre-loaded by default on any computers that you buy.
- We can use the operating system that comes with the computer, however, one can upgrade or even change operating systems.
- Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux are the most common operating systems for personal computers.
- Modern operating systems use a graphical user interface or GUI which lets one use the mouse to click icons, buttons, and menus which are clearly displayed on the screen using a combination of graphics and text.
- Each operating system's GUI has its own look and feel.
- Modern operating systems use the basic principles and are user-friendly.
Single-tasking
- It can run only one program at a time.
- This is achieved by time-sharing
- Time is divided between the available processor and the processes.
- With help of a task-scheduling subsystem of the OS, the processes that are interrupted repeatedly in time slices.
Multi-tasking
- It allows more than one program to run at a time.
- There are two principles that are preemptive and co-operative types.
- In preemptive multitasking – OS slices the CPU time and dedicates a slot for each of the programs.
- Cooperative multitasking – OS relays on each process to provide time to the other processes in a defined manner.
Single-User
- The single-user operating system runs only for one user.
- However, at times it may allow multiple programs to run at the same time.
Multi-User
- A multi-user operating system extends the basic concept of multi-tasking with facilities that identify processes and resources.
- For example – the data to be processed and stored on a disk, the system permits multiple users to interact with the system at the same time.
- For efficient use of the system, OS schedule task by time-sharing.
Distributed
- These are OS which manages a group of individual computers and makes them appear to be a single computer.
- These computations can be carried out on more than one machine.
- A distributed system is nothing but when the group of computers work in cooperation supporting one another.
Templated
- Templated OS creates a single virtual machineimage and works as a guest operating system.
- These data are then saved as a tool for multiple running virtual machines.
- This is commonly used in large server warehouses.
- They are also used both in virtualization and cloud computing management.
Embedded
- These are designed to be used in embedded computers.
- It operates easily on small machines like PDAs.
- They can be operated with a limited number of resources.
- Usually very compact and extremely efficient by design.
- Examples are - Windows CE and Minix 3
Real-time
- This OS guarantees to process data by a specific moment in time.
- A real-time operating system may be single-tasking or multi-tasking.
- While multitasking, it uses specialized scheduling algorithms so that a deterministic nature of behaviour is achieved.
- When it switches between tasks based on their priorities or external events then it operates by an event-driven system.
- By a time-sharing operating systems switch tasks based on clock interrupts.
Library
- A library operating system works as networking.
- These are provided in the form of libraries and composed with the application and configuration code to construct a unikernel.
- These are a specialized, single address space, machine image that can be deployed to the cloud or embedded environments.
Uses of an operating system
- It manages resources like processor, files, memory and device.
- It acts as an interface between the user and the machine.
- It is a platform for executing various application programs.
- It secures the programs and performs input/output operations.
- It makes the communication possible with another process running within the system.
- In case of failed execution, the operating system itself takes appropriate action.
Recap
On any computer, an operating system is the most important software as it manages all software and hardware on the computer.
Functions of the operating system
- Processor management
- Memory management
- File management
- Device management
Types of operating systems
- Single-tasking
- Multi-tasking
- Single-User
- Multi-User
- Distributed
- Templated
- Embedded
- Real-time
- Library