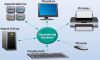
A network can be simply defined as a group of computers and other devices connected in order to exchange data.
Each of the devices on the network can be thought of as a node; each node has a unique address, which is a numeric quantity.
Example: 204.160.241.98
There are two principle kinds of networks
Wide Area Networks (WANs) and Local Area Networks (LANs)
Wide Area Networks (WANs)
- Wide area network spreads to a larger extent
- It covers cities, countries, and continents.
- It works based on packet switching technology.
- Examples: Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)
Local Area Networks (LANs)
- Local area network provides coverage to the smaller extent
- It covers buildings or a set of closely related buildings.
- Examples: Ethernet, Token Ring, and Fiber Distributed Data Interconnect (FDDI).
Ethernet LANs – It is a broadcast communication based on a bus topology.
Token ring LANs – This is based on a ring topology.
FDDI LANs – It works based on the token ring mechanism where two rings flow in the opposite directions and use optical fiber.
Protocols –
- They define the set of rules that govern the communications between two computers connected to a network.
- The main purpose of a protocol is to address and route the messages, detect the error and recover, sequence and flow controls etc.
- It contains the syntax, which defines the format of the messages exchanged, and the semantic, which specifies the action taken by each entity when specific events occur.
- Example: HTTP protocol for communication between web browsers and servers.
OSI Layers
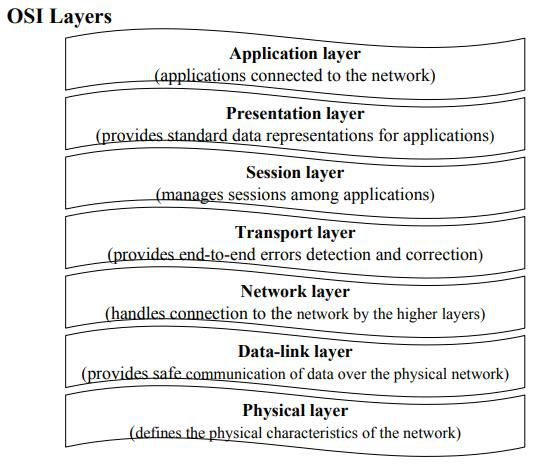
Physical layer –
- It ensures that the data is shared in a safe and efficient way.
- It uses electronic circuits for data transmission.
Data link layer –
- It is responsible for data encapsulation.
- Data encapsulation is done in the form of packets.
- It is used for interpretation at the physical layer.
Network layer –
- The main purpose is to transmit packets from a source A to a destination B.
Transport layer –
- It is useful to delivery the packets from a source A to a destination B.
Session layer –
- It is responsible for the management of network access.
Presentation layer –
- It determines the format of the data transmitted to applications.
- It also helps in data compressing/decompressing, encrypting etc.
Application layer –
- This layer contains the applications which are used by the end-user.
- Applications such as Java, Word, PowerPoint, etc.
TCP/IP Model
The TCP/IP Model –
Consists of only 4 layers they are:
- Application layer
- Transport layer
- Internet layer
- Network layer
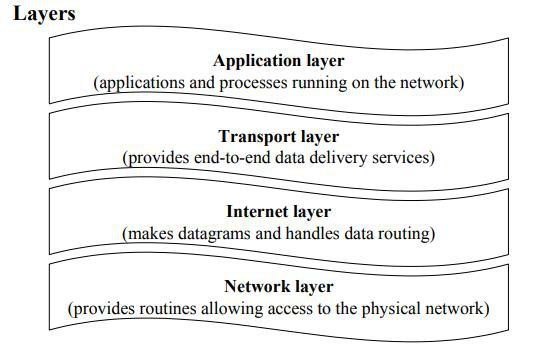
Network layer
- Performs the same function as the physical, the data link and network layers in the OSI model.
- Its main function is to map the IP addresses and network physical addresses.
- Encapsulation of IP datagrams
- Example – formation of packets, which will be understandable by the network.
Internet layer
- It usually lies at the heart of TCP/IP.
- It provides the frame for transmitting data from place A to place B.
- Data transmission is based on the Internet Protocol (IP).
Transport layer
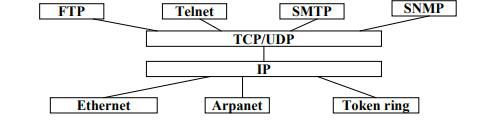
- Works based on two main protocols which are TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram protocol)
Application layer
- Performs the same function as application, presentation, and session layers of the OSI layers.
- Protocols involved in this layer: HTTP, FTP, SMTP etc.
Internet Protocol (IP) –
Internet protocol has main two functions, such as
→ It decomposes the initial information flow into packets of standardized size and then reassembles at the destination.
→ It also routes a packet through networks, from the source to the destination which is identified by its IP address.
→ Also the transmitted packets are not guaranteed to be delivered (datagram protocol).
→ Each datagram will have a header including IP address and port number of the destination.
→ Datagrams are then sent to selected gateways
→ E.g. IP routers, connected at the same time to the local network and to an IP service provider network.
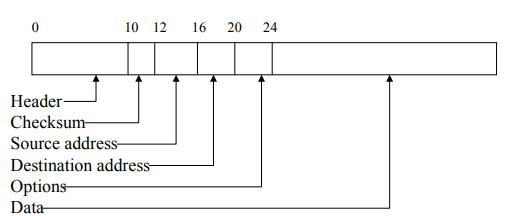
Structure of an IP packet –
- The field at the beginning of the packet is called the header.
- It defines the IP protocol’s functionality and limitations.
- For encoding source and destination addresses, we have 32 bits, each of these holds address fields.
- The remainder of the header (16 bits) encodes various information such as the total packet length in bytes.
- Hence all IP packets can be a maximum of 64Kb long.
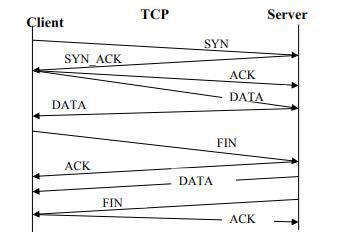
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) –
→ TCP guarantees safe delivery, error detection, safe data transmission and assures that data is received in the correct order with help of IP.
→ It also requires that the computers communicating establish a connection (connection-oriented protocol) before sending the data.
User Datagram Protocol (UDP) –
→ Datagram protocols are built on top of IP which is useful for sending small size data.
→ It has the same packet-size limit (64Kb) as IP but allows for port number specification.
→ It provides 65,536 different ports and every machine has two sets of 65,536 ports which are specified one for TCP and the other for UDP.
→ Without any further verification, it provides support only for data transmission from one end to the other.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) –
- FTP allows transferring collection of files between two machines which are connected to the Internet.
Telnet (Terminal Protocol) –
- Mainly used to connect to a remote host in terminal mode.
NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) –
- This allows organizing communication groups among specific topics.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) –
- This is the basic service for electronic mails (e-mails).
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) –
- This takes care of the management of the network.
Recap
Networking
A network can be simply defined as a group of computers and other devices connected in order to exchange data.
There are two principle kinds of networks
Wide Area Networks (WANs) and Local Area Networks (LANs)
OSI Layers
Functions of data transmission through OSI layers
TCP/IP Model
Consists of only 4 layers they are:
- Application layer
- Transport layer
- Internet layer
- Network layer
Structure of an IP packet
TCP / UDP